
FAQ About The Cultural Significance of Traditional Mediterranean Diet in Art and Heritage
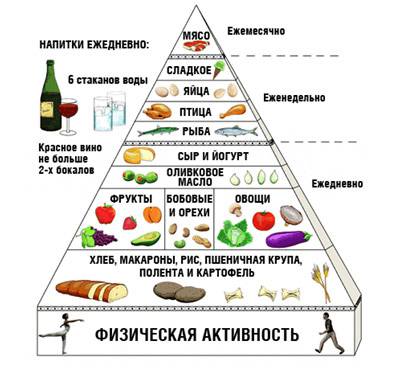
What is the Traditional Mediterranean Diet?
The Traditional Mediterranean Diet is a dietary pattern that emphasizes consumption of plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and legumes. It includes olive oil as the primary fat source, moderate intake of fish and poultry, and a low consumption of red meat and dairy products. Wine is consumed in moderation, often with meals.

How does the Mediterranean Diet influence Mediterranean art?
The Mediterranean Diet influences art by being a frequent subject and medium in regional artworks. Its elements, such as fruits, vegetables, and olive trees, are often depicted in paintings, mosaics, and sculptures, symbolizing prosperity, health, and joy. This diet reflects a lifestyle deeply ingrained in Mediterranean culture, which is portrayed in various art forms.

What are some traditional Mediterranean dishes depicted in art?
Traditional Mediterranean dishes appearing in art include olives and olive oil, bread and cheese, figs, and wine. These items are often found in still-life paintings and are imbued with symbolic meanings, representing themes such as abundance, spirituality, and the cycle of life. Such culinary depictions celebrate both the aesthetic and nutrition values of these foods.

Why is olive oil considered significant in Mediterranean heritage?
Olive oil holds a central place in Mediterranean heritage due to its historical, cultural, and economic significance. Used in cooking, religious rituals, and medicine, it symbolizes prosperity and health. It has been cultivated since ancient times, and its production is intertwined with the social and economic life of Mediterranean regions, often celebrated in festivals and artworks.

How do social practices in the Mediterranean region reflect the traditional diet?
Social practices in the Mediterranean region, such as communal meals and food-related festivals, reflect the traditional diet. Meals are often social occasions, emphasizing the importance of shared dining experiences in building community ties. Festivals celebrating harvests and specific foods, like grape or olive festivals, highlight the cultural significance of the Mediterranean diet.

What role does wine play in Mediterranean cultural practices?
Wine plays a significant role in Mediterranean cultural practices as a symbol of hospitality, celebration, and religious traditions. It is often consumed during meals, festivals, and ceremonies, marking important life events or communal gatherings. Wine's history in the region is rich, with its production and consumption practices passed down through generations and depicted in art and literature.

How has the Mediterranean Diet influenced Western cuisine?
The Mediterranean Diet has had a profound influence on Western cuisine, known for introducing healthy eating practices emphasizing fresh, seasonal ingredients. The diet's emphasis on olive oil, herbs, and grains has been integrated into various culinary traditions worldwide, promoting a balanced eating pattern associated with numerous health benefits.

What are the health benefits associated with the Mediterranean Diet?
The health benefits of the Mediterranean Diet include reduced risks of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. It is associated with promoting longevity and overall well-being due to its high intake of antioxidants, healthy fats, and fiber. This dietary pattern supports cardiovascular health and a balanced lifestyle.

How is Mediterranean cuisine represented in regional cultural heritage sites?
Mediterranean cuisine is represented in cultural heritage sites through historic marketplaces, traditional farms, and olive oil mills. Sites like these offer insights into ancient agricultural practices and food production techniques. Additionally, UNESCO has recognized the Mediterranean Diet as part of Intangible Cultural Heritage, highlighting its importance in the region's identity and history.

What is the significance of communal dining in Mediterranean cultures?
Communal dining is significant in Mediterranean cultures as it reinforces family dynamics, community bonds, and cultural continuity. Shared meals are seen as a time for connection and celebration, and they often feature traditional Mediterranean foods. This practice underscores the social and cultural importance of the diet beyond nutrition alone.

How do culinary traditions in the Mediterranean region impact local economies?
Culinary traditions in the Mediterranean region have a substantial impact on local economies through agriculture, tourism, and gastronomy. The production of staples like olive oil, wine, and grains supports agricultural jobs. Additionally, food tourism attracts visitors interested in experiencing traditional diets, contributing to local economic growth and cultural exchange.

What festivals celebrate traditional Mediterranean foods?
There are numerous festivals celebrating traditional Mediterranean foods, such as the Festa del Redentore in Italy, which includes a feast featuring local produce and seafood. Greece's Olives and Olive Oil Festival highlights the significance of olives in Greek culture. These festivals play a role in preserving cultural heritage and promoting regional diets.

How has literature from the Mediterranean region portrayed the traditional diet?
Literature from the Mediterranean region often portrays the traditional diet as a central element of cultural identity and everyday life. Works by authors like Homer, Dante, and García Lorca include references to meals and foods, using them as metaphors for hospitality, abundance, and cultural continuity. Such portrayals reinforce the cultural significance of dietary practices.

What misconceptions exist about the Mediterranean Diet?
Common misconceptions about the Mediterranean Diet include the belief that it is a uniform diet followed by all Mediterranean countries. In reality, it varies significantly, as each country incorporates its own unique ingredients and recipes. Another misconception is that it includes a high amount of pasta and bread, while the diet actually focuses on whole grains, vegetables, and healthy fats.

How do Mediterranean culinary traditions influence family life?
Mediterranean culinary traditions greatly influence family life by fostering daily rituals centered around food and dining. Family meals are pivotal in strengthening familial relationships and passing down cultural values and traditions. Cooking together and sharing meals are ways families connect, celebrate, and preserve their cultural heritage.

What role does seafood play in the Mediterranean Diet and culture?
Seafood is integral to the Mediterranean Diet and culture, offering a primary source of lean protein and omega-3 fatty acids. Culturally, it represents a connection to the sea, which is central to life in coastal communities. Traditional dishes featuring seafood are celebrated in festivals and reflect the diet's emphasis on health and sustainability.

How do traditional Mediterranean diets adapt to modern culinary practices?
Traditional Mediterranean diets adapt to modern culinary practices by incorporating contemporary health trends while maintaining core principles of the diet. Chefs often innovate by adding new flavors and techniques, yet they preserve the focus on fresh, local, and seasonal ingredients. This blend of tradition and modernity helps sustain the diet's relevance today.

What is the UNESCO designation for the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean Diet has been recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity. This designation acknowledges not only the diet's nutritional benefits but also its cultural significance, highlighting practices such as family meals, knowledge of crops, and traditional fishing and harvesting methods, all of which contribute to Mediterranean cultural identity.

How do ancient Mediterranean art and artifacts reflect dietary practices?
Ancient Mediterranean art and artifacts often reflect dietary practices through depictions of banquets, food offerings, and agricultural scenes. These artworks provide insights into the food production, consumption habits, and social status associated with different foods. Statues, pottery, and frescoes illuminate how vital the diet was to social and cultural life in antiquity.

Why is bread symbolically important in Mediterranean culture?
Bread holds symbolic importance in Mediterranean culture as a staple food that represents sustenance, hospitality, and communal sharing. It is often central in religious rituals and ceremonies, seen as both a sacred and everyday food. Bread-making traditions are passed through generations, reinforcing cultural identity and the continuity of culinary heritage.
